Images are more powerful than words in today's content-based digital world. Whether it’s for blogs, websites, branding, or creative exploration, the demand for high-quality images has grown exponentially. Traditionally, producing such visuals required skilled designers, stock image subscriptions, or photography sessions. But now, with the power of generative AI, you can create professional-grade visuals from simple text inputs.
Among the rising stars in the AI image generation field is Bria AI, and its Bria 2.3 model is particularly suited for building custom image generation applications. This post will walk through how to create your AI-powered image generator using Bria 2.3, complete with a user interface built with Streamlit, and data handled through secure API practices.
What is Bria AI?
Bria AI is a generative visual AI platform designed to meet the creative and commercial needs of businesses. Established in 2020, it has rapidly evolved into a versatile toolset for enterprises and content creators alike, offering:
- Text-to-image generation
- Background removal and editing
- Inpainting (image modification)
- Advanced image control tools like ControlNet
More importantly, Bria distinguishes itself by its ethics-first approach. Unlike many generative AI platforms that rely on questionable data scraping practices, Bria trains its models exclusively on licensed and compensated content. Its partnership with Getty Images is a testament to its commitment to responsible AI usage—helping businesses generate visuals without crossing legal or ethical boundaries.
Why Bria 2.3 is a Game-Changer?

Bria 2.3 is the latest and most advanced model released by the company. It has been designed to push the envelope in terms of both speed and quality, giving developers and businesses a powerful tool for producing stunning images in seconds.
Here’s what makes Bria 2.3 stand out:
- Faster processing time for image generation
- Higher resolution outputs and better detail handling
- Improved control over generation parameters like style, aspect ratio, and visual composition
- Optimized for enterprise-grade scalability, making it viable for commercial production
Bria 2.3 isn’t just a tech upgrade—it’s a solution for organizations that need high-volume, customizable visuals without compromising on ethics or quality.
Getting Started with Bria 2.3 via NVIDIA NIM
To use Bria 2.3, you’ll need access to the NVIDIA Inference Microservice (NIM), which provides API access to Bria's capabilities. Signing up through NVIDIA’s developer portal gives you a key to interact with the Bria model programmatically. The goal is to develop a lightweight image generation web application that accepts a user’s description, sends it to Bria’s API, and displays the AI-generated image—all in real-time.
Step-by-Step: Building Your Image Generator App
Below, this post outline how to create a fully functional app with the following stack:
- Python for core scripting
- Streamlit for the front-end interface
- Dotenv for managing sensitive credentials
- Requests to communicate with the API
- Base64 for decoding image output
Step 1: Setting Up the Environment
Before diving into code, set up your working environment. Install the necessary Python packages:
pip install streamlit python-dotenv requests
Create a .env file in your project directory to store your API key securely:
NVIDIA_API_KEY=your_actual_api_key_here
Keeping API keys outside your code is a best practice that prevents security breaches and accidental key sharing.
Step 2: Writing the App Logic
Start by importing the required libraries and loading your API key:
import os
import time
import base64
import requests
import streamlit as st
from dotenv import load_dotenv
Load environment variables and configure the API endpoint:
load_dotenv()
API_KEY = os.getenv("NVIDIA_API_KEY")
API_URL = "https://ai.api.nvidia.com/v1/genai/briaai/bria-2.3"
HEADERS = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_KEY}",
"Accept": "application/json"
}
This block initializes the app’s connection to Bria’s service via the NVIDIA endpoint.
Step 3: Designing the User Interface
Use Streamlit to craft a basic front-end for your app. It will allow users to input prompts and select options like aspect ratio:
st.set_page_config(page_title="Bria AI Image Generator")
st.title("AI Image Generator with Bria 2.3")
user_prompt = st.text_input("Describe the image you want to generate:")
aspect = st.selectbox("Select Aspect Ratio", ["1:1", "16:9", "4:3"])
generate = st.button("Generate Image")
When the button is clicked, the app sends a request to the Bria API with the user’s input.
Step 4: Sending the Request and Handling the Response
Now, set up the logic to send the request and handle the API’s base64 image response.
if generate and user_prompt.strip():
params = {
"prompt": user_prompt,
"cfg_scale": 5,
"aspect_ratio": aspect,
"seed": 0,
"steps": 30,
"negative_prompt": ""
}
with st.spinner("Generating image..."):
start = time.time()
res = requests.post(API_URL, headers=HEADERS, json=params)
duration = time.time() - start
if res.status_code == 200:
data = res.json()
image_b64 = data.get("image")
if image_b64:
image_bin = base64.b64decode(image_b64)
output_path = "output.png"
with open(output_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(image_bin)
st.image(output_path, caption="Your Generated Image")
st.success(f"Image created in {duration:.2f} seconds")
else:
st.error("No image data returned from the server.")
else:
st.error(f"Request failed: {res.status_code}")
This code:
- Sends the user’s prompt to Bria
- Waits for the AI to generate the image
- Decodes the base64 image
- Saves it locally
- Displays it within the app
If something goes wrong (e.g., missing image data or a failed request), the app notifies the user with a clear message.
Step 5: Running Your Application
To run the application, use this terminal command:
streamlit run your_script_name.py
Replace your_script_name.py with the name of your Python file. Once it launches, a browser window will open, allowing you to test image prompts in real time.
Example Prompt
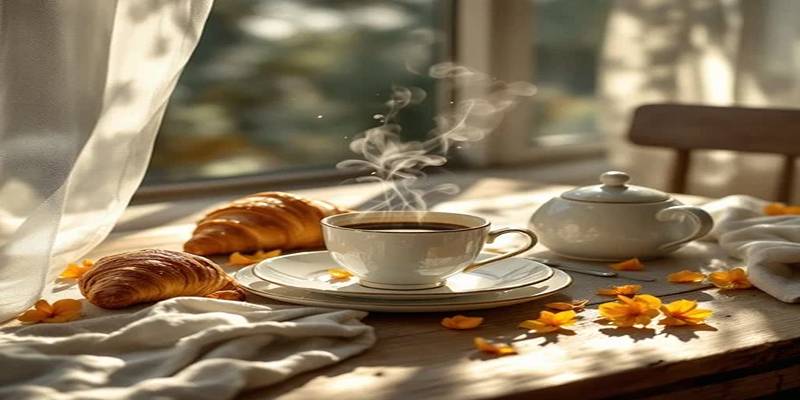

Try using the following prompt in your app:
"A cozy café with a steaming coffee cup, rustic wooden table, croissant, and sunlight pouring in through the window"
It will generate a warm, photorealistic scene—perfect for blogs, Instagram posts, or marketing visuals.
Conclusion
Building your own AI image generation app is no longer the realm of large tech firms. Thanks to platforms like Bria and accessible tools like Streamlit, anyone with basic Python knowledge can create intelligent, user-friendly applications. The Bria 2.3 model, in particular, provides a powerful, ethical, and high-performance solution for generating realistic images from simple descriptions. By wrapping that functionality in a simple app, you’ve now got a custom tool that can be used for design, branding, or just creative fun. Take the time to experiment with prompts, polish your interface, and explore the deeper API settings—this project is just the beginning.